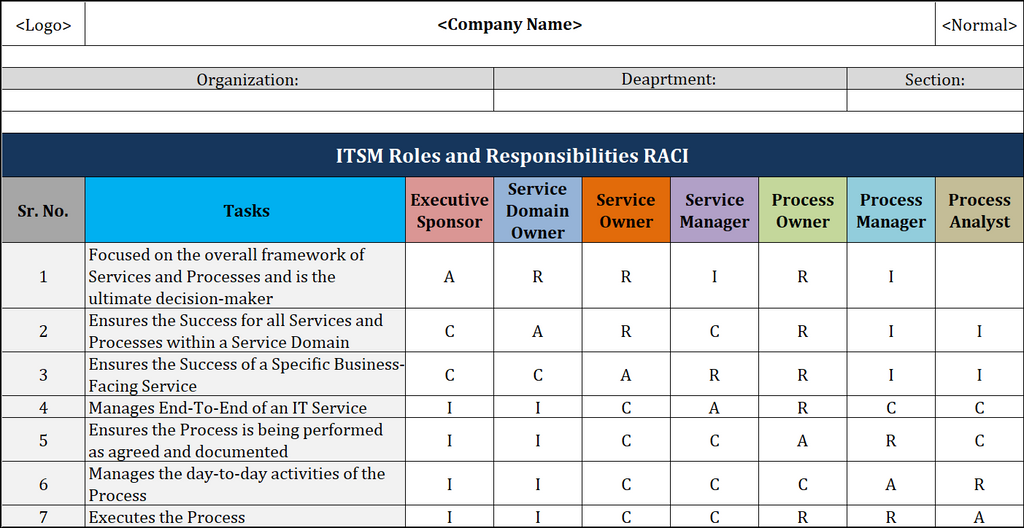
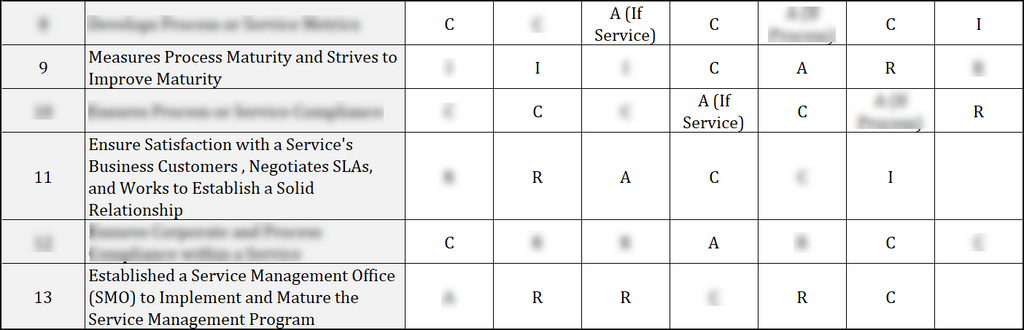
RACI For ITSM Roles And Responsibilities Template
Introduction
The RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) matrix for IT Service Management (ITSM) roles and responsibilities in IT Governance is a powerful tool that provides clarity and structure to the various tasks and processes within an IT organization. This template outlines and defines the key roles involved in ITSM activities, specifying who is Responsible for executing tasks, who is Accountable for overall outcomes, who needs to be Consulted for input, and who should be informed about progress. By leveraging the RACI matrix, IT Governance ensures that each team member understands their role, responsibilities, and interactions with others, promoting effective collaboration, accountability, and streamlined decision-making in the dynamic landscape of IT services and management.
The Need For Clear Roles And Responsibilities In ITSM
Clear roles and responsibilities in IT Service Management (ITSM) are imperative for several reasons:
1. Efficient Operations:
- Clearly defined roles ensure that each team member understands their specific responsibilities and tasks.
- This clarity helps streamline day-to-day operations, reducing confusion and enhancing overall efficiency.
2. Accountability:
- Clear roles designate individuals who are accountable for specific outcomes or processes.
- Accountability fosters a sense of ownership, encouraging team members to take responsibility for their tasks and deliverables.
3. Effective Collaboration:
- Well-defined roles facilitate collaboration by specifying who is responsible for what.
- Teams can work more cohesively, avoiding duplication of efforts and ensuring that tasks are completed in a coordinated manner.
4. Improved Communication:
- Knowing who needs to be consulted or informed in various processes promotes effective communication.
- Team members are aware of their role in the information flow, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings and communication gaps.
5. Customer Satisfaction:
- Clear roles contribute to the consistent delivery of services, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
- When responsibilities are well understood, it is more likely that services are provided in a timely and reliable manner.
6. Risk Management:
- Defined roles help identify potential points of failure or bottlenecks in processes.
- It enables organizations to proactively manage risks by ensuring that critical tasks have dedicated responsible parties.
7. Adaptability To Change:
- As IT environments evolve, clear roles make it easier to adapt to changes in technologies, processes, or team structures.
- When roles are well-defined, it becomes more straightforward to incorporate new responsibilities or adjust existing ones.
8. Training And Development:
- Roles and responsibilities provide a framework for training programs and professional development.
- Individuals can focus on acquiring skills relevant to their roles, contributing to both personal and organizational growth.
Key ITSM Roles And Responsibilities
1. Service Desk Analyst
Responsibilities:
- Respond to and resolve user incidents and service requests.
- Log and categorize incidents, ensuring accurate and timely documentation.
- Provide first-line support and escalate issues as needed.
2. Incident Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Oversee the entire incident management process.
- Ensure timely resolution of incidents and minimize service disruptions.
- Analyze incident trends and recommend preventive measures.
3. Change Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Control and manage changes to the IT environment.
- Assess and prioritize change requests.
- Minimize the impact of changes on services and systems.
4. Problem Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Investigate and diagnose the root causes of recurring incidents.
- Implement solutions to prevent the recurrence of problems.
- Maintain a proactive approach to problem management.
5. Service Level Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Define, negotiate, and manage service level agreements (SLAs).
- Monitor and report on service performance against SLAs.
- Identify areas for service improvement.
6. Configuration Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Maintain a centralized configuration management database (CMDB).
- Control and document changes to the IT infrastructure.
- Ensure accurate and up-to-date configuration information.
7. Release Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Planned, scheduled, and controlled the release of changes to the production environment.
- Coordinate with different teams to ensure smooth release processes.
- Conduct post-implementation reviews for continuous improvement.
8. IT Security Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Implement and enforce security policies and procedures.
- Monitor and respond to security incidents.
- Conduct risk assessments and implement security controls.
9. Capacity Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Forecast and plan for future capacity requirements.
- Monitor and analyze system performance.
- Optimize resource utilization to meet business demands.
10. Availability Manager:
Responsibilities:
- Ensure that IT services meet agreed-upon availability targets.
- Plan and implement measures to prevent and minimize service outages.
- Conduct availability and reliability assessments.
Creating a RACI Matrix for ITSM
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a RACI matrix for ITSM:
Step 1: Identify ITSM Processes And Activities
- List ITSM Processes: Identify the key ITSM processes relevant to your organization (e.g., Incident Management, Change Management, Problem Management).
- Break Down Processes: Break down each process into specific activities or tasks. For example, within Incident Management, tasks could include incident logging, categorization, resolution, and closure.
Step 2: Define Roles Associated with Each Process/Activity
- Identify Key Roles: Determine the roles involved in each ITSM process. Common roles include Service Desk Analyst, Incident Manager, Change Manager, Problem Manager, etc.
- Map Roles To Activities: Assign each role to the activities they are responsible for. For instance, the Incident Manager may be responsible for the overall Incident Management process.
Step 3: Assign RACI Values for Each Role
1. Define RACI Categories:
- Responsible (R): The person or role responsible for performing the task.
- Accountable (A): The person ultimately accountable for the task's success. Only one 'A' per task.
- Consulted (C): Individuals or roles that need to provide input or expertise.
- Informed (I): Individuals or roles that need to be kept in the loop but don't directly contribute.
2. Assign RACI Values:
- Go through each task/activity and assign the appropriate RACI values to each role.
- Use "R," "A," "C," and "I" to indicate the level of involvement for each role in each task.
Step 4: Collaborate With Stakeholders
- Validate Assignments: Review the RACI matrix with relevant stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Address Concerns: Address any concerns or conflicts that arise during the validation process.
Step 5: Document and Communicate
1. Create The RACI Matrix:
- Use a spreadsheet or dedicated RACI template to document the matrix.
- Organize tasks vertically and roles horizontally.
2. Communicate Roles And Responsibilities:
- Share the finalized RACI matrix with the entire IT team.
- Ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
Step 6: Periodic Review And Update
- Establish Review Schedule: Set a regular schedule for reviewing and updating the RACI matrix (e.g., quarterly or as needed).
- Incorporate Changes: Update the matrix to reflect changes in processes, tasks, or team structure.
Step 7: Integrate RACI Matrix Into ITSM Processes
1. Incorporate Into Workflows:
- Embed the RACI matrix into ITSM workflows and documentation.
- Ensure that team members reference the matrix in their daily activities.
Conclusion
The RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) Matrix emerges as a cornerstone in the realm of IT Service Management (ITSM), providing a structured and transparent framework that significantly enhances organizational effectiveness. By clearly delineating roles and responsibilities, the RACI Matrix not only minimizes confusion and ambiguity but also cultivates a culture of accountability and ownership among team members. The improved communication and collaboration it fosters contribute to more efficient decision-making and streamlined processes, ultimately enhancing the agility of ITSM operations. As a dynamic tool, the RACI Matrix proves invaluable in navigating the ever-evolving landscape of IT, offering adaptability and clarity crucial for sustained success in managing IT services within an organization.




