A Guide to IT Controls
An IT infrastructure is a complex data, applications, and tools framework. Ensuring an organization's IT technology is functional, robust, and safe is essential. IT controls are policies seen as an assurance of well-maintained IT technology. It is proof of a structured IT infrastructure that provides reliable data, complies with regulation policies, and governs applications.
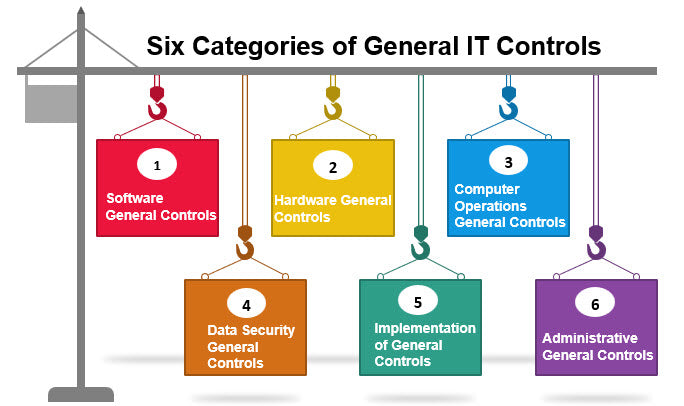
What are the Six Categories of General IT Controls?
Information Technology General Controls (ITGC) establish guidelines for technology usage in an organization by creating rules to prevent data leaks, theft, or network disruptions. There are six types of general controls: software, hardware, computer operations, data security, implementation, and administrative.
1. Software General Controls :
Software controls handle the system software operations and minimize unauthorized access to software platforms, systems, and computer functions. It is a crucial tool that manages various programs storing and studying datasets.
2. Hardware General Controls :
Enterprises use hardware controls to ensure physically strong hardware and well-functional applications. Physical computer equipment is susceptible to damage in natural disasters or extraordinarily high or low temperatures. With the help of hardware control, companies can keep their equipment safe and establish backup and recovery procedures.
3. Computer Operations General Controls :
This ITGC category manages the operation processes of computer systems by monitoring data storage and processing. It ensures data is stored and processed in the correct and assigned data points by performing various check-ups, such as setting up computer programming tasks and implementing backup and recovery systems for inconsistent or defective operations.
4. Data Security General Controls :
IT data contains private and confidential client or business information, making it susceptible to breaches. Given the highly classified nature of files, organizations require a solid security framework to guard the data. Data security controls protect crucial business information on disks and prevent unauthorized access, damage, or data modification.
5. Implementation of General Controls :
ITGCs come in handy during internal audits and inspections. Implementation controls audit a computer’s system and processes across multiple platforms to ensure the reliability and management of operations. It thoroughly checks for comments and reviews left by users and teams during a process’s lifecycle and user participation at each level.
It ensures a well-structured cost-benefit system is in place to enhance system development. Since an audit conducts a control and quality check, implementation controls oversee program schedules, conversion, system testing, and reports and logs.
6. Administrative General Controls :
An administrative control manages a computer system’s standards, policies, guidelines, rules, and framework to ensure the correct implementation and enforcement of IT tools and applications.
What are the Five Types of Input Validation?
Organizations acquire and process data from various sources. However, not every dataset is secure or required. Input validation is a regular system check-up that studies datasets obtained from unknown or unfamiliar sources before processing them. It uses coding software to scan data according to the prescribed rules. There are five input validation categories: accuracy, business guidelines, warnings, IT security, and risk management.
1. Accuracy :
Runs basic commands to check the validity of incoming data if it performs its assigned role. For instance, if the system performs numerical functions, accuracy checks whether the acquired data contains numerical values or not.
2. Business Guidelines :
Business guidelines gauge the reliability of data per the established set of rules and policies. For instance, if the rules assign a specific period in the future for a particular action, business guidelines reject the data if its time of action does not match the period mentioned in the guidebook.
3. Warnings :
During unpredictable or inconsistent operations, warnings notify users of the unstable or irregular data state, preventing organizations from acquiring weak datasets.
4. Information Security :
Information security studies data and ensures it does not carry threats, such as data breaches, fraud, or viruses, before accepting it.
5. Risk Management :
Risk management scans and identifies potential risks, such as financial threats, audit trail fraud, unrecognized authentication, and asset security.
What are IT Controls in Audit?
IT controls, or ITGCs, are general controls that monitor IT systems, such as applications, data, infrastructure, security, and operating systems, to ensure their functionality. ITGCs maintain the strength and integrity of operations, processes, and data that form the core of IT systems. There are various forms of ITGCs, including:
- Granted and authorized access to IT applications, data, and infrastructure to prevent unapproved changes and modifications.
- Program change and management change controls
- Data and system backup and recovery procedures
- Computer operation controls
- Data points controls
- Security and safety controls
- System schedule and lifecycle management
What are the Examples of IT Control?
Information Technology controls are procedures and policies created to meet and comply with proposed and desired IT goals, such as regulatory compliance, risk management, and application management. Some examples of Information Technology controls are:

(i) Audit Reports :
Audit reports generate logs of users’ IP addresses with accurate timestamps, details, and relevant data.
(ii) Change Management :
An IT system consists of multiple project elements that depend on each other for smooth and seamless operations. Change management observes and handles three types of project baseline to monitor the system lifecycle and progress: schedule, cost, and scope.
(iii) Capacity Management :
Capacity management allows an organization to control its business processes and operations. This process ensures that IT services are readily and constantly available and meet business and client requirements while complying with the internationally set ISO standards.
(iv) Incident Management :
The incident management process develops high-quality tools and equipment to boost an organization’s productivity and service quality. This process delivers customer requests across service management points to restore services to their default and actual performance.
(v) Problem Management :
As a vital component of Information Technology Service Management (ITSM), the problem management process identifies and reduces potential and frequent incidents that affect ITSM’s infrastructure. It spots and eliminates solutions by devising effective solutions that find gaps in system operations, affect customer satisfaction, and damage IT services.
Why are IT Controls Important?
ITGCs benefit organizations in a myriad of ways, such as:
(i) Identifying Potential Threats :
Most IT operations are performed on the cloud or other online platforms. Since sensitive information, such as financial data, account transactions, client details, and employee information, transfer through IT systems, ITGCs create a robust security system to identify and remove potential and existing threats.
(ii) System Evaluation :
System evaluations are essential to ensure the IT infrastructure runs smoothly and efficiently. Information Technology controls conduct systematic checks to ensure all operations are up-to-date and well-maintained.
(iii) IT Governance :
Through IT governance, ITGCs maintain the integrity, structure, frameworks, and practices that support and enhance an organization’s processes, helping it reach its business objectives.
Final Thoughts :
IT Controls are rules and policies that oversee an IT system’s infrastructure and status. It ensures a company’s IT operations run per regulatory compliance policies, keep data secure, bolster controls, and assist in IT auditing.

