Risk Treatment Plan: Understanding The Importance Of Risk Treatment and Its Effectiveness
Any successful business strategy must include risk management. To minimize risks and their impact, organizations must create a comprehensive plan for risk management. This plan will outline the strategies and tactics to be used in order to manage and address identified risks.
By proactively managing risks and developing effective risk management strategies, organizations can protect their assets, business reputation, and operations. This article will discuss the importance of developing a risk management plan and what elements should be included.
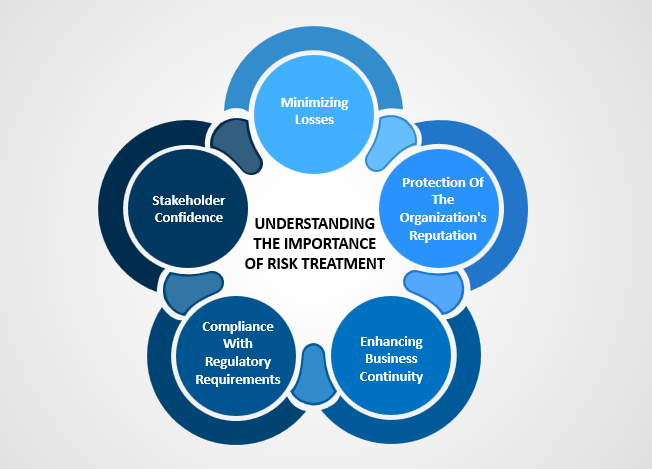
Understanding the Importance of Risk Treatment
To manage risks efficiently, organizations must realize the importance of developing a treatment plan for risk. This section explains why a treatment plan for risk is important to protect an organization's reputation, assets, and business operations.
1. Minimizing Losses: A risk management plan has as one of its primary goals to reduce potential losses that could arise from risks identified. Implementing appropriate risk management can help organizations reduce the impact and likelihood of adverse events. This proactive approach safeguards the financial resources of businesses, their investments, and their profitability.
2. Protection Of The Organization's Reputation: A solid plan for risk management helps protect the reputation of the organization. A proactive approach to risk management allows organizations to identify potential risks and deal with them before they become significant issues. This helps preserve their reputation and credibility in the eyes of stakeholders.
3. Enhancing Business Continuity: Disruptions to business operations can be severe for an organization. A risk management plan will ensure that the appropriate measures are taken to minimize the impact of natural catastrophes, supply-chain disruptions, or cyber-attacks. Organizations can minimize disruptions and ensure uninterrupted operations by identifying risks and creating contingency plans.
4. Compliance With Regulatory Requirements: Many industries have different regulatory requirements. A comprehensive risk management plan considers the legal and regulatory environment in which an organization operates. By implementing compliance strategies and addressing compliance risks, the organization can avoid potential legal penalties, reputational damages, and business disruptions.
5. Stakeholder Confidence: A robust plan for risk management demonstrates an organization's commitment to ensuring the well-being of all stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and shareholders. Organizations can instill confidence in their stakeholders by actively managing risks and implementing the appropriate measures. This will foster stronger relationships and business success in the long term.
Assessing and Identifying Risks
Organizations must identify and evaluate potential risks before implementing a treatment plan. This step is crucial in developing a risk-management strategy that prioritizes resources and efforts and helps develop an effective risk-management strategy.
Here are some of the key elements that go into identifying and assessing risk:
1. Risk Identification: The initial step in risk management is identifying potential risks that may impact an organization. It involves a comprehensive analysis of the external and internal factors that may pose a risk. Internal risks include inefficiency, human error, or inadequate cybersecurity, while external risks can range from natural disasters, economic downturns, and regulatory changes to market volatility. To ensure a holistic perspective, it's important to include key stakeholders from various departments or business units.
2. Risk Assessment: After identifying the risks, organizations must assess their likelihood and impact. The risk assessment involves assessing the likelihood of the risk happening and the potential consequences for the organization. This assessment should take into account factors like the severity of impact, frequency of risk occurrence, and the organization's tolerance for risks. Risks can be evaluated using qualitative and quantitative methods, such as risk matrices and scenario analyses. By assigning a score or rating to each risk, organizations can focus their attention and resources on the greatest risks.
3. Documentation Of Risks: It is important to document in a centralized and structured manner the risks identified and their assessment results. This documentation is a useful reference for all parties involved in the process of risk management and helps to facilitate effective communication and decision-making. The risk register, or risk inventory, should contain information about the risks, their potential consequences, their likelihood and severity, and any control measures or mitigation strategies in place.
4. Risk Mitigation and Control: Once the risks are identified and assessed, organizations can implement risk mitigation and control. These measures are intended to reduce or eliminate the impact and likelihood of identified risks. Regularly review and monitor the effectiveness of these actions to ensure they remain suitable and effective.
5. Risk Monitoring: Organizations must constantly monitor and review the risk landscape. Regular risk assessments, audits, and external reviews can help to achieve this.
By identifying and assessing risk effectively, organizations can gain a thorough understanding of potential threats. The foundation of proactive risk management is identifying and assessing risks. This ensures that organizations are prepared to navigate the constantly changing business landscape.
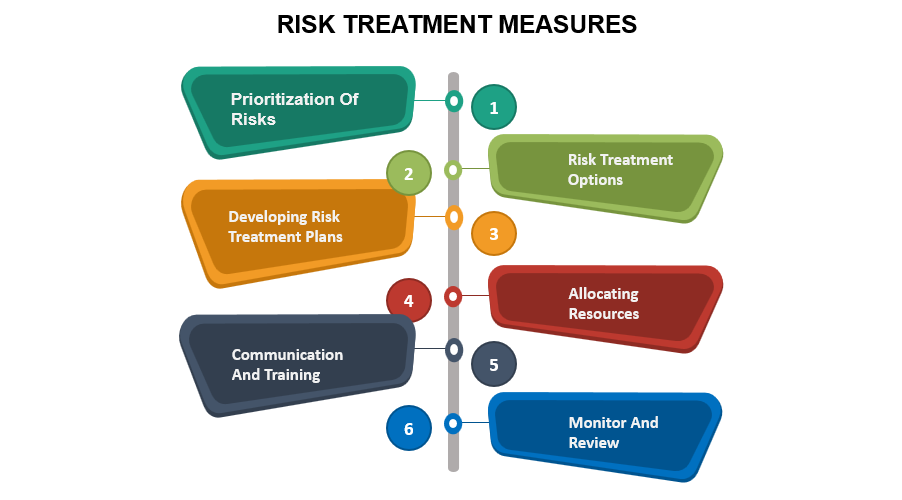
Implementing Risk Treatment Measures
The next step in the process of risk management is the implementation of appropriate risk treatment. These measures are intended to control or mitigate the identified risks and reduce their impact on the organization.
Considerations and steps to implement risk treatment measures:
1. Prioritization of Risks: After assessing the risks, it's important to rank them according to their importance and impact. Not all risks require the same amount of attention or immediate action. Prioritizing risks allows organizations to allocate resources.
Focus on the most important risks and use their resources efficiently.
2. Risk Treatment Options: Different treatment options are available based on the severity and nature of the risk. Standard risk treatment options include:
- Risk Avoidance
- Risk Transfer
- Risk Reduction
- Risk Retention
3. Developing Risk Treatment Plans: Once the treatment options for risk have been identified, organizations need to develop detailed plans of risk treatment. These plans detail the specific strategies and actions to address each risk.
4. Allocating Resources: To implement risk treatment measures, it is necessary to allocate appropriate financial, technological, and human resources. Organizations must ensure they allocate sufficient resources to implement risk treatment plans.
5. Communication and Training: Effective communication and effective training are crucial for successfully implementing risk treatment measures. All stakeholders, including management, employees, and external partners, need to be made aware of the risks and the treatment options selected, as well as their respective roles and responsibilities.
6. Monitor And Review: To ensure that risk treatment measures are effective, they should be continually monitored and reviewed. Regular assessments are needed to assess the progress made in implementing the risk treatment measures, identify any weaknesses or gaps, and make the necessary adjustments.
Implementing effective measures to reduce risk can help organizations address identified risks. Organizations can stay proactive by regularly monitoring and reviewing the risk treatment measures and adapting to the changing risk landscape.
Monitoring the effectiveness of the plan
Once the measures to mitigate risk have been implemented, organizations must continue to monitor and evaluate their effectiveness. Monitoring and reviewing help to ensure that implemented measures are achieving the desired outcomes and effectively mitigating the identified risks.
The following are key steps and considerations for monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of a risk treatment plan.
1. Establish Key Performance Indicators: Organizations must define specific KPIs to evaluate the effectiveness and performance of risk management measures. If the goal is to reduce the risk of data breaches, then a KPI that would be relevant could be the number of successful cyberattacks against the organization's system.
2. Regular Assessments: It is important to conduct regular assessments to measure the effectiveness of risk management measures and evaluate their progress. These assessments can be performed at regular intervals, such as quarterly or annual, depending on the risk nature and the organization's appetite for risk.
3. Identify Weaknesses and Gaps: It is important to identify gaps or weaknesses within the risk management measures implemented. The identification of gaps and weaknesses allows organizations to understand where their implemented measures might fall short and then take corrective action.
4. Make The Necessary Adjustments: The organization should make the necessary adjustments based on their assessment findings. These adjustments should be made to address identified weaknesses and gaps and improve the overall efficacy of the risk management plan.
5. Communication and Reporting: Communication is essential in monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of a risk management plan. This ensures transparency and lets all stakeholders know about the organization's efforts to manage risk.
Organizations can manage identified risks more effectively by monitoring and reviewing risk treatment plans. The monitoring and reviewing process must be ongoing to ensure that the risk management program is effective and protects the assets, reputation, and business operations of an organization.
Conclusion
Monitoring and reviewing the plan's risk treatment is essential for organizations in order to ensure that the measures implemented are effective. Organizations can improve the overall effectiveness of their plans by establishing specific KPIs and conducting regular assessments.
Regular communication with all stakeholders and regular reporting help maintain transparency and keep everyone updated about the results and progress of the risk management plan. External reviews and feedback can offer valuable insight and suggestions for improvement.


