ISO 27001:2022 Cryptographic Controls Policy Template Download
The ISO 27001 Cryptographic Controls Policy is designed to ensure organizations use secure and effective cryptographic methods in their information security strategies. The use of mathematical techniques and algorithms to convert data into unreadable formats, or ciphertext, is part of cryptography. This helps to maintain confidentiality and integrity.The Cryptographic Controls Policy is a framework that provides guidelines for the management of cryptographic keys, protocols, algorithms and usage across an organization. The policy lays out guidelines and procedures to implement cryptographic solutions that comply with the organization's objectives for security and industry best practices.
Cryptographic Controls are Important in Protecting Sensitive Data
ISO 27001-based information security management systems (ISMSs) include cryptographic controls that are crucial to protecting sensitive data. These controls use encryption and cryptographic methods to protect data and communication from unauthorized access and interception.This is a summary of the importance of cryptographic control in protecting sensitive information:
- Confidentiality : Cryptographic controls provide confidentiality by encrypting sensitive information, rendering it useless and unreadable to unauthorized parties or attackers. Even if a hacker gains access to encrypted information, they will not be able to decipher it unless they have the cryptographic key.
- Integrity : Cryptographic controls maintain data integrity by using cryptographic hashing and digital signatures. Digital signatures and cryptographic hashing ensure that data is not altered during transmission or storage.
- Authentication: Cryptographic control mechanisms enable strong authentication through the use cryptographic keys or certificate. This allows only authorized users and systems to access sensitive data, adding another layer of security against unauthorized access.
- Protection against Insider Threats : Cryptographic controls help protect sensitive data from insider threats. They do this by ensuring only users who have the cryptographic keys are able to access it. This prevents data breaches, and the unauthorized disclosure of data by employees or privileged user.
- Secure Data Transmission : When sensitive data is sent over networks or internet, cryptographic controls such as SSL/TLS ensure the data remains confidential.
- Compliance Requirements : Many data protection laws and industry regulations, including GDPR, HIPAA and PCI DSS mandate the use cryptographic controls in order to protect sensitive information. Cryptographic controls help organizations meet these regulatory requirements.
- Protection against Cyberattacks: Cryptographic controls are a powerful line of defense in the face of cyberattacks such as data breaches, ransomware and man-in-the middle attacks. Encryption prevents attackers from accessing sensitive data, even if they breach other security measures.
The Key Components to an Effective Cryptographic Controls Policy
A cryptographic control policy that is effective in ISO 27001 must include comprehensive guidelines and procedures for the implementation and management of cryptographic mechanisms within an organization's Information Security Management System (ISMS).Here are some of the main components that you should include in a policy like this:
- Password protection: Outline guidelines to secure passwords by using cryptographic hashing. Specific requirements for salting and strong password policies.
- Integrity Control: Stress the importance of data integrity by using cryptographic methods such as digital signatures or hash functions.
- Approved Method of Search: Define methods authorized for searching and retrieving data encrypted. Make sure that sensitive data is protected during searches.
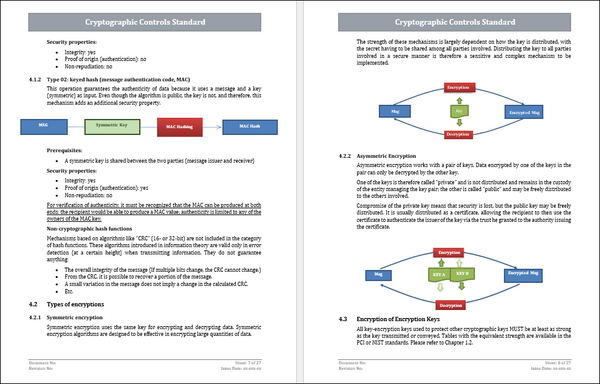
- Asymmetric Encryption : Describe how to use asymmetric cryptography (public key) for secure key exchanges, digital signatures and confidentiality. Key pairs, encryption and verification are discussed.
- Hardware Security Modules: Use HSMs to secure key management, and perform cryptographic operations. Explain how they can enhance the security of cryptographic control.
- Integrity Control: Reiterate the importance of cryptographic control in maintaining data integrity and preventing unauthorized modification.
- Password Authentication & Storage: Describe secure methods of password authentication and storage including salting, hashing and MFA.
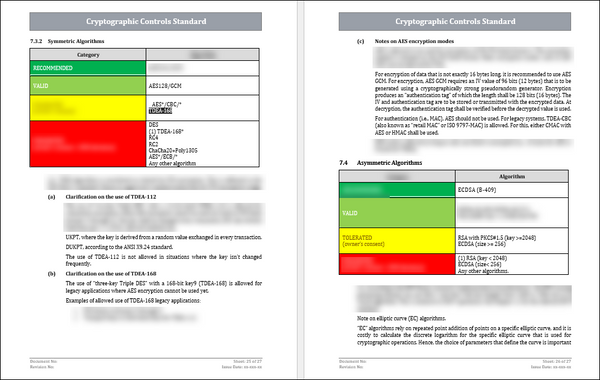
- Algorithm selection: Give guidance on choosing appropriate cryptographic algorithms depending on the security requirements and data to be protected.
Employee Awareness and Training on Cryptographic Controls
The training and awareness of employees about cryptographic controls is crucial to ensuring that the Information Security Management System based on ISO 27001, which includes cryptographic measures, is implemented and used properly.How to train employees and increase awareness:
- Training Sessions: Hold training sessions for employees to inform them of the importance and role of cryptographic controls in protecting sensitive data. These sessions can either be led by experts in internal security or consultants with experience in cryptography.
- Relevance for Employees: Stress how cryptographic controls impact the work of employees and their overall security. Explain how digital signatures and encryption ensure authenticity in documents or data transmission.
- Real-Life Scenarios : Use real-life examples and scenarios to illustrate the importance of cryptographic control in protecting sensitive data and preventing data breaches.
- Hands-on Exercises : Include hands-on exercises and simulations that allow employees to practice the use of cryptographic tools. This practical approach reinforces learning and builds confidence when applying cryptographic controls.
- Best Practices & Guidelines: Educate your employees about industry best practices, including how to choose strong encryption algorithms, exchange secure keys, and store secure keys.
- Cryptographic Key Management : Explain the importance of proper cryptographic management including generation of strong keys, securely distributing them and storing and rotating them.