GDPR Response to DSAR Template
Overview
DSAR - A Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) is a fundamental right granted to individuals under data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. DSARs allow individuals, known as data subjects, to request access to the personal data that organizations are processing. DSARs empower individuals to understand how their data is used and ensure that organizations comply with data protection regulations.
GDPR - The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection regulation enacted by the European Union to enhance the protection of individuals' data and privacy. It came into effect on May 25, 2018, and applies to any organization that processes the personal data of EU residents, regardless of the organization's location.
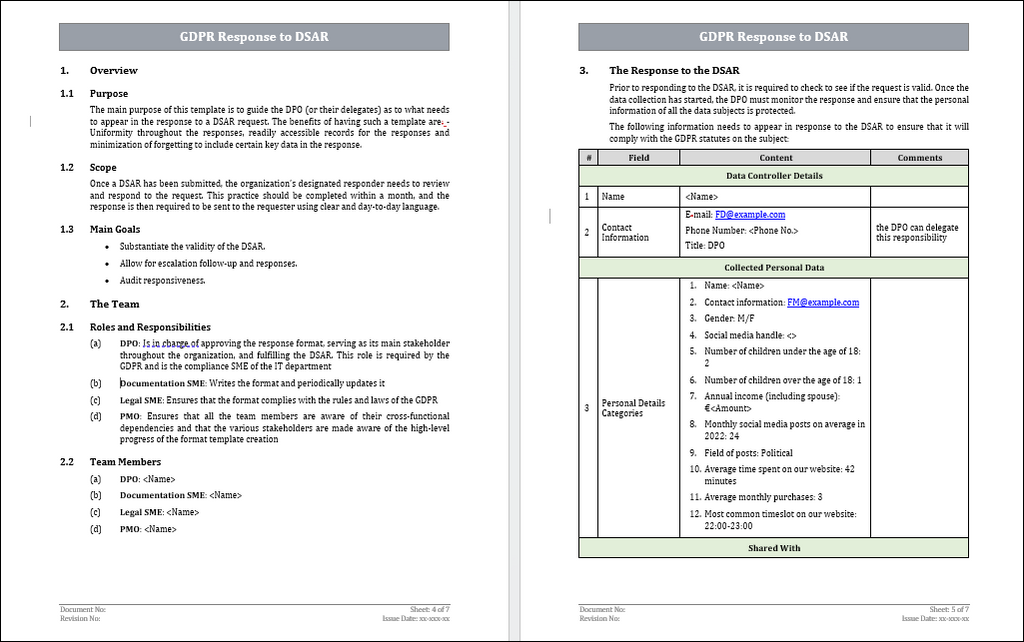
Here Are Some Of The Key Details About DSARs and GDPR:
DSARs:
1. Individuals have the right to request access to the personal data that a company or organization holds.
2. The company or organization must respond to the DSAR within one month of receiving it.
3. The company or organization must provide the individual with a copy of their personal data in a format they can easily understand.
4. The company or organization may charge a reasonable fee for DSAR processing.
GDPR:
1. The GDPR applies to all organizations that process the personal data of individuals in the EU.
2. The GDPR requires organizations to comply with several requirements, including,
- Getting people's permission before using their personal info.
- Assuring the lawful and equitable processing of personal data.
- Guarding against the misuse, access, and disclosure of personal data.
- Erasing personal data when it's no longer required.
What Are DSARs?
A Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) is a request made by an individual to access their personal data that a company or organization holds. DSARs are a right under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a European Union (EU) law that applies to all organizations that process the personal data of individuals in the EU.
The GDPR gives individuals several rights concerning their personal data, including the right to:
- Access their personal data.
- Rectify their personal data.
- Erasure of their personal data
- Restriction of processing of their personal data
- Portability of their personal data
- Not to be subject to automated decision-making
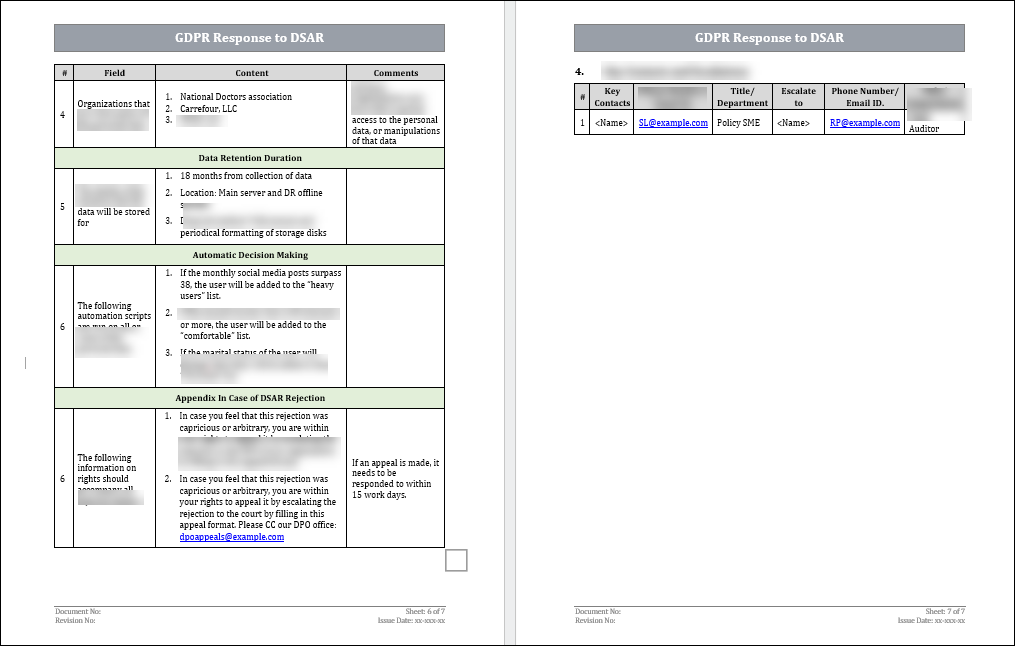
What Details/Actions Must You Include In Your DSAR Response? Who Are The Beneficiaries Of DSARs?
Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs) beneficiaries are individuals whose personal data is being processed by organizations and various stakeholders who aim to uphold data protection and privacy rights. Here's a brief overview of the beneficiaries of DSARs:
1. Data Subjects (Individuals): DSARs primarily benefit individuals whose personal data is collected and processed by organizations. DSARs empower these individuals to access their data, understand its use, and ensure its accuracy and lawful processing.
2. Privacy Advocates and Organizations: Individuals and organizations advocating for privacy rights and data protection benefit from DSARs as they help individuals exercise their rights and promote transparent data processing practices.
3. Data Protection Authorities: Regulatory bodies responsible for enforcing data protection laws benefit from DSARs as they use them to monitor organizations' compliance and ensure that individuals' rights are upheld.
4. Legal Professionals: Lawyers and legal experts benefit from DSARs by assisting individuals in exercising their rights, navigating data protection regulations, and ensuring that organizations follow legal requirements.
5. Consumer Protection Groups: Organizations focused on consumer rights benefit from DSARs as they align with their goals of ensuring fair treatment and transparency in data processing.
Who Can Submit A DSAR?
A Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) can be submitted by individuals whose personal data is being processed by organizations. In the context of data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European
Union, the term "data subject" refers to the individual to whom the personal data relates. Therefore, a DSAR can be submitted by:
1. Data Subjects (Individuals): Data Subjects refer to any individual whose personal data is being processed by an organization that has the right to submit a DSAR. This includes customers, clients, employees, users, patients, students, and anyone whose personal data is collected and stored.
2. Authorized Representatives: In some instances, individuals may authorize a representative to submit a DSAR on their behalf. This could be a legal guardian, parent, or authorized agent.
3. Parents or Legal Guardians: When processing personal data of minors, parents or legal guardians may submit DSARs on behalf of their children.
4. Deceased Individuals' Representatives: In some jurisdictions, individuals with legal authority, such as executors of a deceased person's estate, may submit DSARs regarding the deceased person's data.
How Can Data Subjects Submit DSAR?
Data subjects can submit a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) to an organization through various methods, depending on the organization's processes and the available communication channels. Here are common ways that data subjects can submit DSARs:
1. Written Request:
Data subjects can send a written request by mail or email to the organization's designated contact address for DSARs. The request should clearly state that it is a DSAR and provide the necessary details to identify the data subject.
2. Online Forms:
Many organizations provide online forums on their websites that data subjects can use to submit DSARs. These forms may prompt the data subject to provide the necessary information for verification.
3. Customer Service Channels:
Data subjects can contact the organization's customer service department or designated DSAR contact to initiate the request verbally or through written communication.
4. Dedicated DSAR Email Address:
Some organizations have a dedicated email address for DSARs. Data subjects can send their DSAR requests to this email address, ensuring that the request is directed to the appropriate team.
5. Personal Accounts:
In cases where data subjects have personal accounts on websites or platforms, they can initiate DSARs directly from their accounts, allowing them to access and manage their personal data.
Organizations must respond to DSARs within the time frame mandated by data protection regulations, typically within one month. They must verify the data subject's identity before disclosing any personal data to ensure the security and privacy of the information.
How To Prepare For DSARs?
1. Document Your Data Processing Activities: It would help if you documented all your data processing activities, including the types of personal data you collect, the purposes for which you collect and use the personal data and the third parties with whom you share the personal data. This documentation will be helpful if you receive a DSAR to easily identify the personal data you need to provide to the requester.
2. Create A DSAR Process: You should create a process for responding to DSARs that is clear, concise, and easy to follow. This process should include steps for:
- Receiving the DSAR
- Evaluating the DSAR
- Identifying the personal data that needs to be provided.
- Providing the personal data to the requester
- Documenting the response
3. Train Your Staff: You should train your staff on how to respond to DSARs. This training should cover the following topics:
- The GDPR's requirements for responding to DSARs.
- Your company's DSAR process
- How to identify and collect the personal data that needs to be provided in response to a DSAR
- How to communicate with DSAR requesters
Who Responds to a DSAR?
A Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) is typically responded to by the organization that collects and processes the individual's personal data. The responsibility for responding to a DSAR often falls within the purview of several roles within the organization:
1. Data Protection Officer (DPO):
If your organization requires a Data Protection Officer (DPO) under data protection regulations such as GDPR, the DPO may oversee and coordinate the response to DSARs. The DPO ensures that the organization's DSAR procedures comply with relevant laws.
2. Privacy or Compliance Team:
Organizations often have dedicated privacy or compliance teams handling data protection matters. This team may oversee the processing of DSARs, including verification, data retrieval, and response.
3. Legal Department:
The legal department may review DSAR requests, ensure that responses align with legal requirements, and provide guidance on sensitive data or legal issues.
Key Takeaways
- The request must be complied with promptly.
- It must be in understandable everyday language.
- A copy must be saved for audit purposes.

